The Middle Passage, 1749
A Spotlight on a Primary Source by Robert Livingston
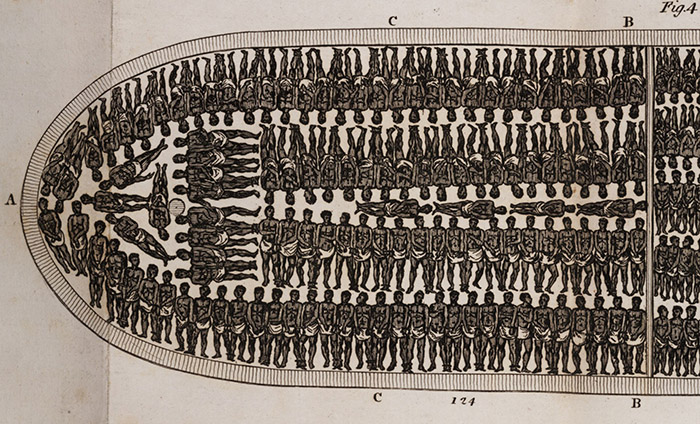 Historians estimate that approximately 472,000 Africans were kidnapped and brought to the North American mainland between 1619 and 1860. Of these, nearly 18 percent died during the transatlantic voyage from Africa to the New World. Known as the "middle passage," this sea voyage could range from one to six months, depending on the weather. On large ships, several hundred slaves could be packed below decks. Branded and chained together, they endured conditions of squalor, and disease and starvation claimed many lives.
Historians estimate that approximately 472,000 Africans were kidnapped and brought to the North American mainland between 1619 and 1860. Of these, nearly 18 percent died during the transatlantic voyage from Africa to the New World. Known as the "middle passage," this sea voyage could range from one to six months, depending on the weather. On large ships, several hundred slaves could be packed below decks. Branded and chained together, they endured conditions of squalor, and disease and starvation claimed many lives.
The closeness of the place, and the heat of the climate, added to the number in the ship, which was so crowded that each had scarcely room to turn himself, almost suffocating us. This produced copious perspirations, so that the air soon became unfit for respiration, from a variety of loathsome smells, and brought on a sickness among the slaves, of which many died, thus falling victims to the improvident avarice, as I may call it, of their purchasers. This wretched situation was again aggravated by the galling of the chains, now become insupportable; and the filth of the necessary tubs [large buckets for human waste], into which the children often fell, and were almost suffocated. The shrieks of the women, and the groans of the dying, rendered the whole a scene of horror almost inconceivable.
In 1748, the sloop Rhode Island, owned by the prominent Livingston family, left New York on a slave trade voyage. It arrived in West Africa on January 18, 1749, and over the next four months Captain Peter James acquired 120 men, women, and children along the African coast. By the time the vessel arrived back in New York in July 1749, "they buryed 37 Slaves & Since 3 more & 2 more likely to die." According to historian Philip Misevich, a loss of 32 percent of the captured people on a voyage was extremely high, and it was therefore most likely a financial disaster for the Livingstons. (Click here for a report on the deaths among Africans on the Rhode Island.)
coast. By the time the vessel arrived back in New York in July 1749, "they buryed 37 Slaves & Since 3 more & 2 more likely to die." According to historian Philip Misevich, a loss of 32 percent of the captured people on a voyage was extremely high, and it was therefore most likely a financial disaster for the Livingstons. (Click here for a report on the deaths among Africans on the Rhode Island.)
On July 29, Robert Livingston reported to Petrus Dewitt on several business dealings—including the loss incurred on the Rhode Island. Livingston’s callous description demonstrates the slave-trade investor’s emphasis on the financial loss rather than the human cost:
We have thank God had the good fortune of haveing one of our Guinea Sloops come in, tho after along passage of 79 days in which time they buryed 37 Slaves & Since 3 more & 2 more likely to die which is an accident not to be helped, and which if had not happend we Should have made a Golden Voyage but as it is there will not be much left I fear, unless the other Sloop meets with better Luck
